Photo by Markus Spiske on Unsplash
In the age of digitalization, huge information have changed the confront of numerous businesses, and sports, including football, is no special case. Football clubs and affiliations are utilising information not as it were to progress their amusement techniques but moreover as an effective device in the commerce angles of sports administration. This article looks at how cutting-edge information analytics advances are utilised to optimize income, brand administration, and fan engagement.
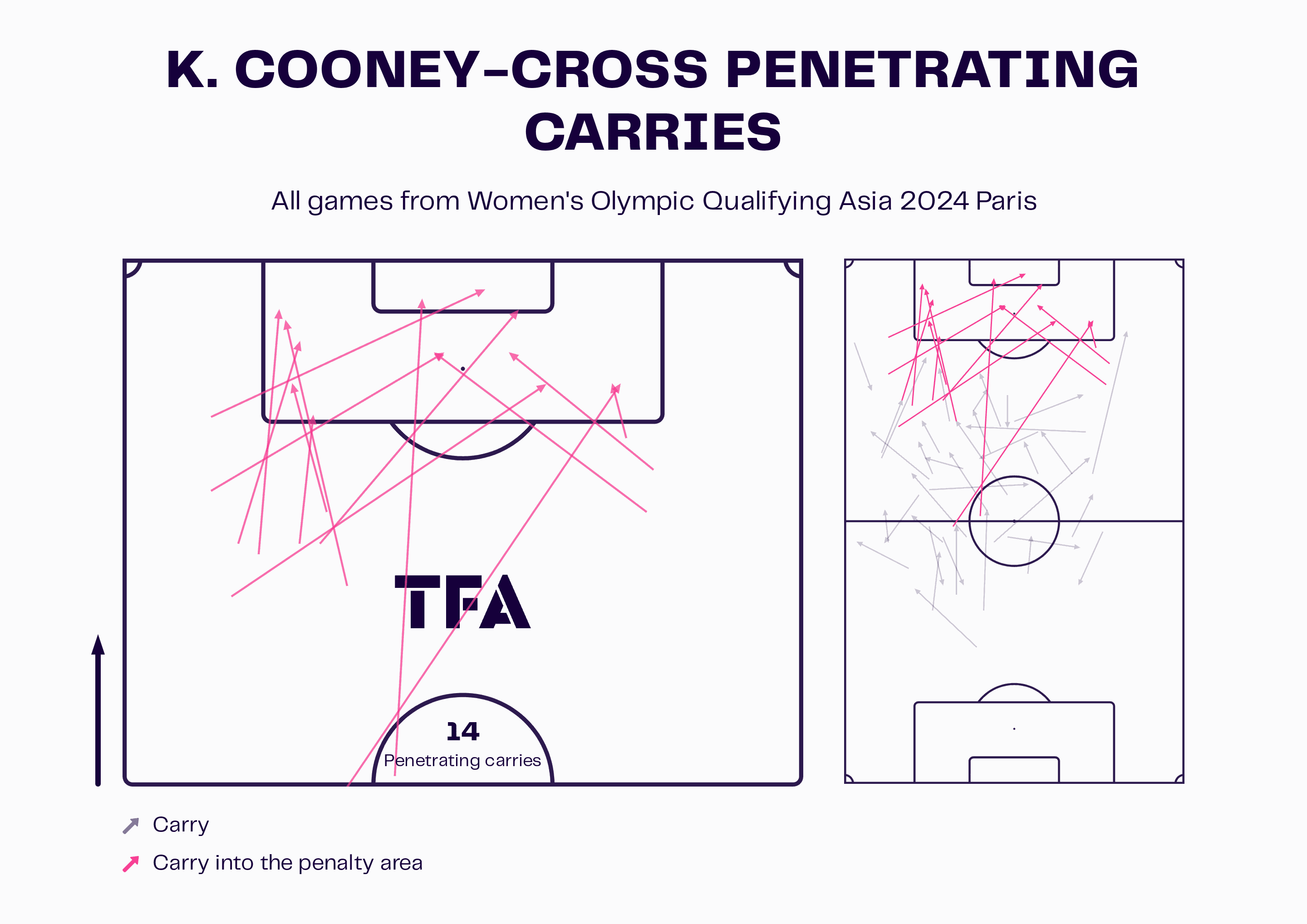
Optimizing performances and strategies
First of all, Big Data allows coaching staff and analysts to dive deeper into the technical aspects of the game. By analyzing thousands of moments from matches, teams can identify the weaknesses of opponents, evaluate the effectiveness of their tactics, and optimize training processes. FC Barcelona, for example, uses analysis tools to measure individual player performance and their contribution to the team game. Here are some key aspects that
Big Data has an impact on:
- Analyzing player performance: Using data to evaluate players’ physical condition, their contribution to attack and defence, and their overall performance on the field.
- Development of game tactics: Creating detailed game plans based on analysing previous opponents’ games, their strengths and weaknesses.
- Optimization of training loads: Adaptation of training programs to the physical condition of players to prevent injuries and maintain optimal fitness.
- Predicting match results: Using statistical models to predict game outcomes to help plan strategies for the season.
Marketing and fan engagement
The use of big data also plays a key role in the marketing strategies of football clubs. Data analysis allows clubs to better understand the preferences and interests of their supporters, optimize marketing campaigns, and even influence decisions on ticket purchases and fan paraphernalia. Through audience segmentation, clubs can create personalized offers, which significantly increase the effectiveness of interaction.
One innovative example is the integration of game mechanics into marketing strategies, for example, the use of virtual realities to create a unique experience for fans. This not only engages the audience but also encourages them to take action, such as using online platforms for fun, such as play roulette online, which can be part of clubs’ promotional campaigns.
Such approaches not only strengthen the connection between the club and its supporters but also open up new commercial opportunities by turning every aspect of the interaction into a potential source of revenue.
Brand and sponsorship management
Big Data is also changing approaches to brand management and sponsor engagement. Football clubs use analytical data to demonstrate their influence and expand their sponsorship portfolios. Not only sports performance is analyzed, but also social media, TV viewing ratings, and other key indicators that help attract new sponsorship contracts and increase the commercial value of the club.
Prediction and risk management
Finally, Big Data provides capabilities for predicting the outcomes of matches and tournaments, which is crucial for betting companies and clubs in terms of risk management. The data collected on past games, player health, and even weather conditions help to form mathematical models for predicting various scenarios. Below is a table showing the typical data used for predictions in football matches:
| Type of Data | Description of Use |
| Game Statistics | Analysis of the number of goals, shots on goal, possession, etc. |
| Medical Data of Players | Assessment of players’ physical condition and injury likelihood. |
| Weather Conditions | Impact of weather on gameplay style and players’ physical condition. |
| Historical Results | Use of the results of previous games to model scenarios. |
Final Thoughts
Big data opens new horizons not only for football clubs but also for the entire sports business. Integrating data analysis technologies allows optimizing everything from game strategies to commercial activities. This confirms that in the modern digital world, information has the status of the most important asset for development and success.




Comments